How to automate UI tests with Github Actions
Developers spend 4-8 hrs a week fixing bugs. Things only get worse if a bug sneaks its way into production. It takes 5-10x longer to fix it. That's why UI testing is integral to delivering high-quality experiences, but it can also be a huge time sink. It's too much work to run all your tests manually after every change.
You can automate your workflow to trigger tests when a developer pushes code. The tests execute in the background and report results on completion. That allows you to detect regressions automatically.
This chapter shows you how to implement such a workflow with Github Actions. Along the way, I'll point out ways to optimize your test runs.
Continuous UI testing
Reviewing code is a big part of being a developer. It helps catch bugs early and maintains high code quality.
To ensure that a pull request (PR) won't break production, you’d typically pull code and run the test suite locally. That disrupts your workflow and takes a lot of time. With Continuous Integration (CI), you get all the benefits of testing without any manual intervention.
You can tweak the UI, build a new feature, or update a dependency. When you open a pull request, the CI server will automatically run comprehensive UI tests—visual, composition, accessibility, interaction and user flows.
You’ll get test results via PR badges, which provide a summary of all the checks.

At a glance, you can tell if the pull request passed all quality checks. If yes, move on to reviewing the actual code. If not, dive into the logs to find out what’s wrong.
"Testing gives me full confidence for automated dependency updates. If tests pass, we merge them in."
— Simon Taggart, Principal Engineer at Twilio
Tutorial
The previous five chapters demonstrated how to test the various aspects of the Taskbox UI. Building on that, we’ll set up continuous integration using GitHub Actions.
Set up CI
Create a .github/workflows/ui-tests.yml file in your repository to get started. A workflow is a set of jobs that you want to automate. It is triggered by events such as pushing a commit or creating a pull request.
Our workflow will run when code is pushed to any branch of our repository and it’ll have three jobs:
- Run interaction and the accessibility tests with the Storybook test runner
- Run visual and composition tests with Chromatic
- Run user flow tests with Cypress
# .github/workflows/ui-tests.yml
name: 'UI Tests'
on: push
jobs:
# Run interaction and accessibility tests
interaction-and-accessibility:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 20
- name: Install dependencies
run: yarn
- name: Install Playwright
run: npx playwright install --with-deps
- name: Build Storybook
run: yarn build-storybook --quiet
- name: Serve Storybook and run tests
run: |
npx concurrently -k -s first -n "SB,TEST" -c "magenta,blue" \
"npx http-server storybook-static --port 6006 --silent" \
"npx wait-on tcp:6006 && yarn test-storybook"
# Run visual and composition tests with Chromatic
visual-and-composition:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0 # Required to retrieve Git history
- name: Install dependencies
run: yarn
- name: Publish to Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# Grab this from the Chromatic manage page
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
# Run user flow tests with Cypress
user-flow:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Install dependencies
run: yarn
- name: Cypress run
uses: cypress-io/github-action@v6
with:
start: npm run dev
Couple of things to note here. For the test runner, we're using a combination of concurrently, http-server and wait-on libraries to build and serve the Storybook to run tests against it.
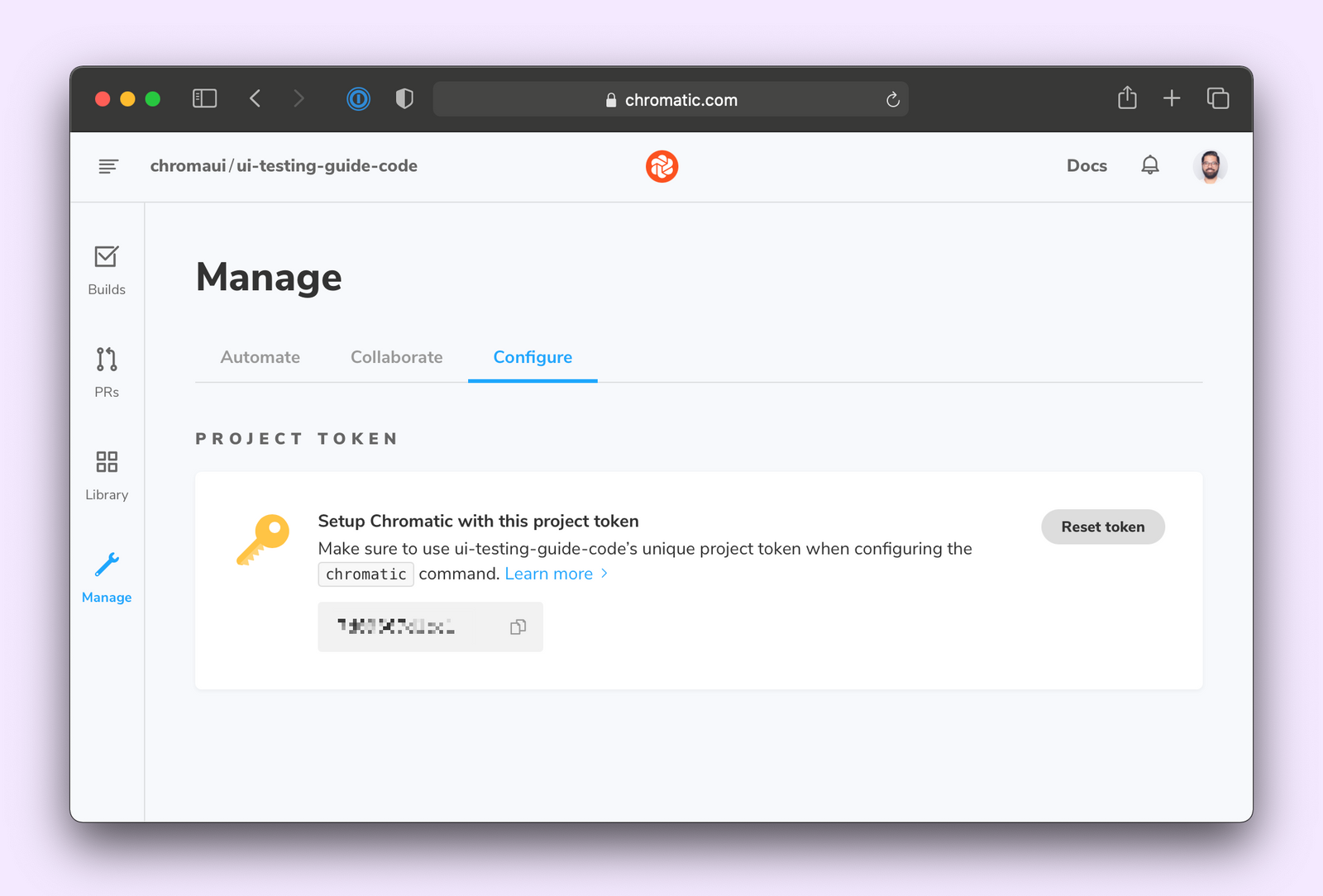
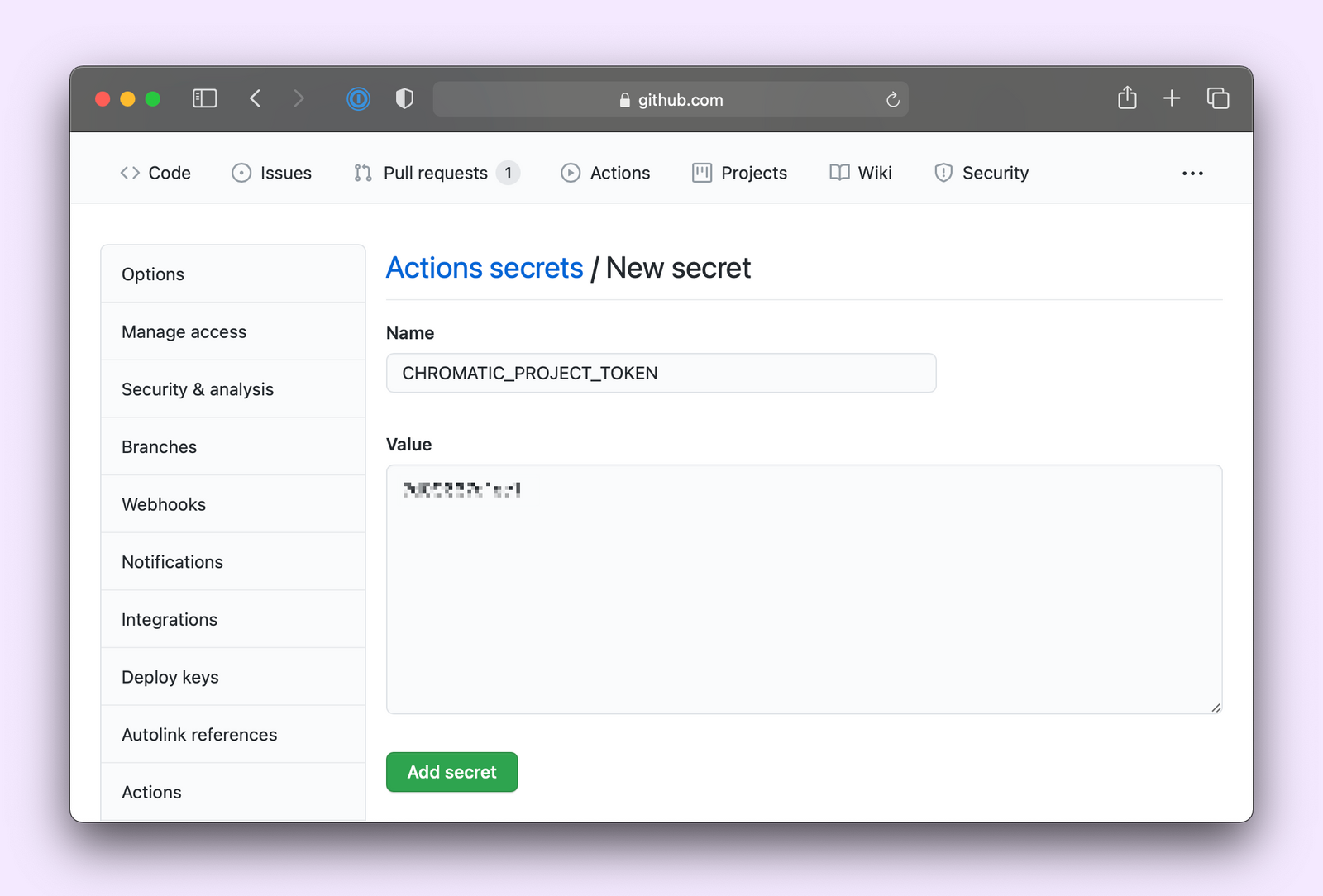
And to run Chromatic, you’ll need the CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN. You can grab it from the Chromatic manage page and add it to your repository secrets.
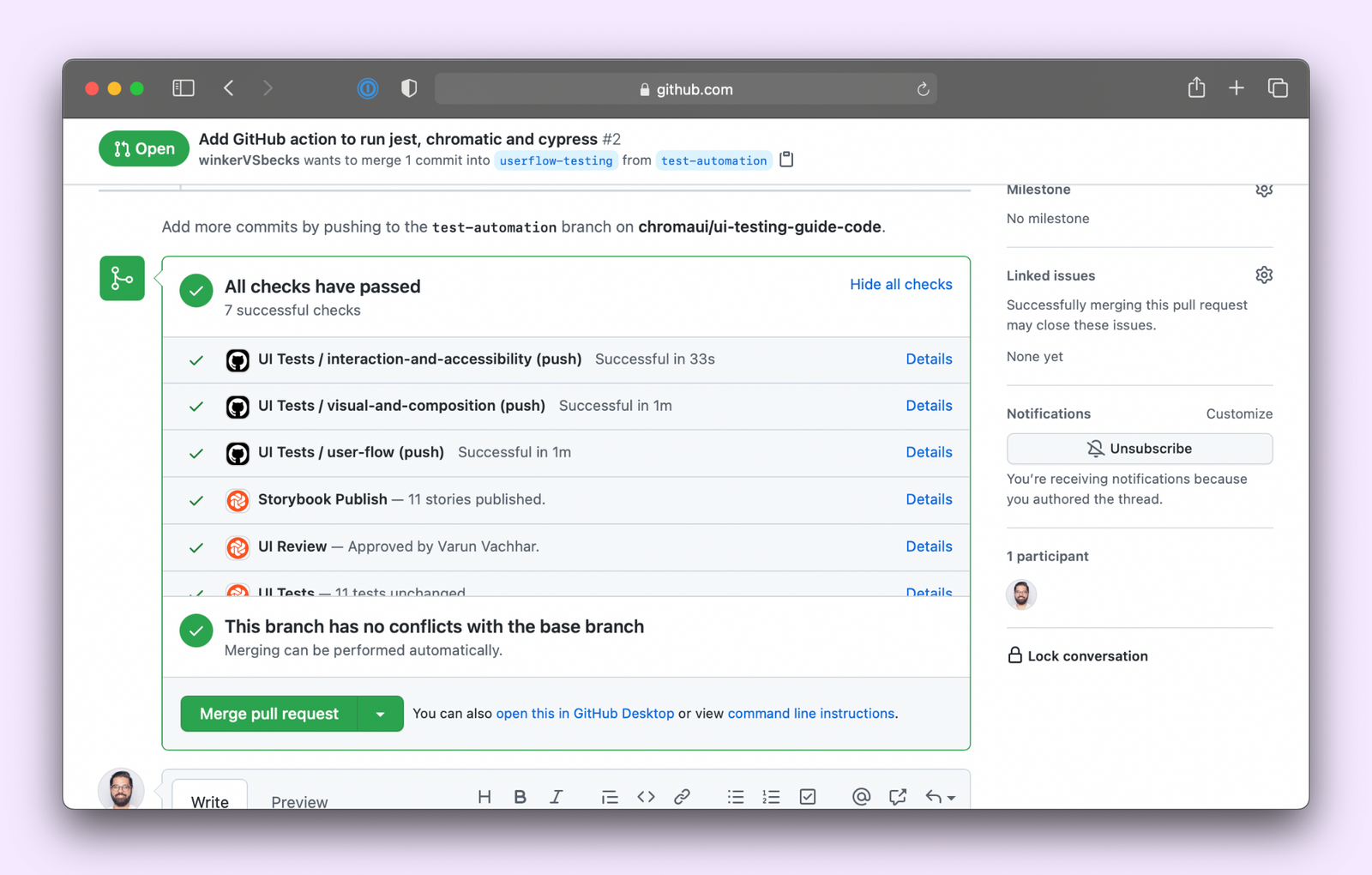
Finally, create a new commit, push your changes to GitHub, and you should see your workflow in action!
Cache dependencies
Each job runs independently, which means the CI server has to install dependencies in all three jobs. That slows down the test run. We can cache dependencies and only run yarn install if the lock file changes to avoid that. Let’s update the workflow to include the install-cache job.
# .github/workflows/ui-tests.yml
name: 'UI Tests'
on: push
jobs:
# Install and cache npm dependencies
install-cache:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Commit
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Cache Yarn dependencies and Cypress
uses: actions/cache@v4
id: yarn-cache
with:
path: |
~/.cache/Cypress
node_modules
key: ${{ runner.os }}-yarn-v1-${{ hashFiles('**/yarn.lock') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-yarn-v1
- name: Install dependencies if cache invalid
if: steps.yarn-cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
run: yarn
# Run interaction and accessibility tests
interaction-and-accessibility:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: install-cache
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 20
- name: Restore Yarn dependencies
uses: actions/cache@v4
id: yarn-cache
with:
path: |
~/.cache/Cypress
node_modules
key: ${{ runner.os }}-yarn-v1-${{ hashFiles('**/yarn.lock') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-yarn-v1
- name: Install Playwright
run: npx playwright install --with-deps
- name: Build Storybook
run: yarn build-storybook --quiet
- name: Serve Storybook and run tests
run: |
npx concurrently -k -s first -n "SB,TEST" -c "magenta,blue" \
"npx http-server storybook-static --port 6006 --silent" \
"npx wait-on tcp:6006 && yarn test-storybook"
# Run visual and composition tests with Chromatic
visual-and-composition:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: install-cache
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0 # Required to retrieve Git history
- name: Restore Yarn dependencies
uses: actions/cache@v4
id: yarn-cache
with:
path: |
~/.cache/Cypress
node_modules
key: ${{ runner.os }}-yarn-v1-${{ hashFiles('**/yarn.lock') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-yarn-v1
- name: Publish to Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# Grab this from the Chromatic manage page
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
# Run user flow tests with Cypress
user-flow:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: install-cache
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Restore Yarn dependencies
uses: actions/cache@v4
id: yarn-cache
with:
path: |
~/.cache/Cypress
node_modules
key: ${{ runner.os }}-yarn-v1-${{ hashFiles('**/yarn.lock') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-yarn-v1
- name: Cypress run
uses: cypress-io/github-action@v6
with:
start: npm run dev
We also tweaked the other three jobs to wait for the install-cache job to complete to use the cached dependencies. Push another commit to re-run the workflow.
Success! You’ve automated your testing workflow. When you open up a PR it’ll run the test runner, Chromatic and Cypress in parallel and display the results on the PR page itself.
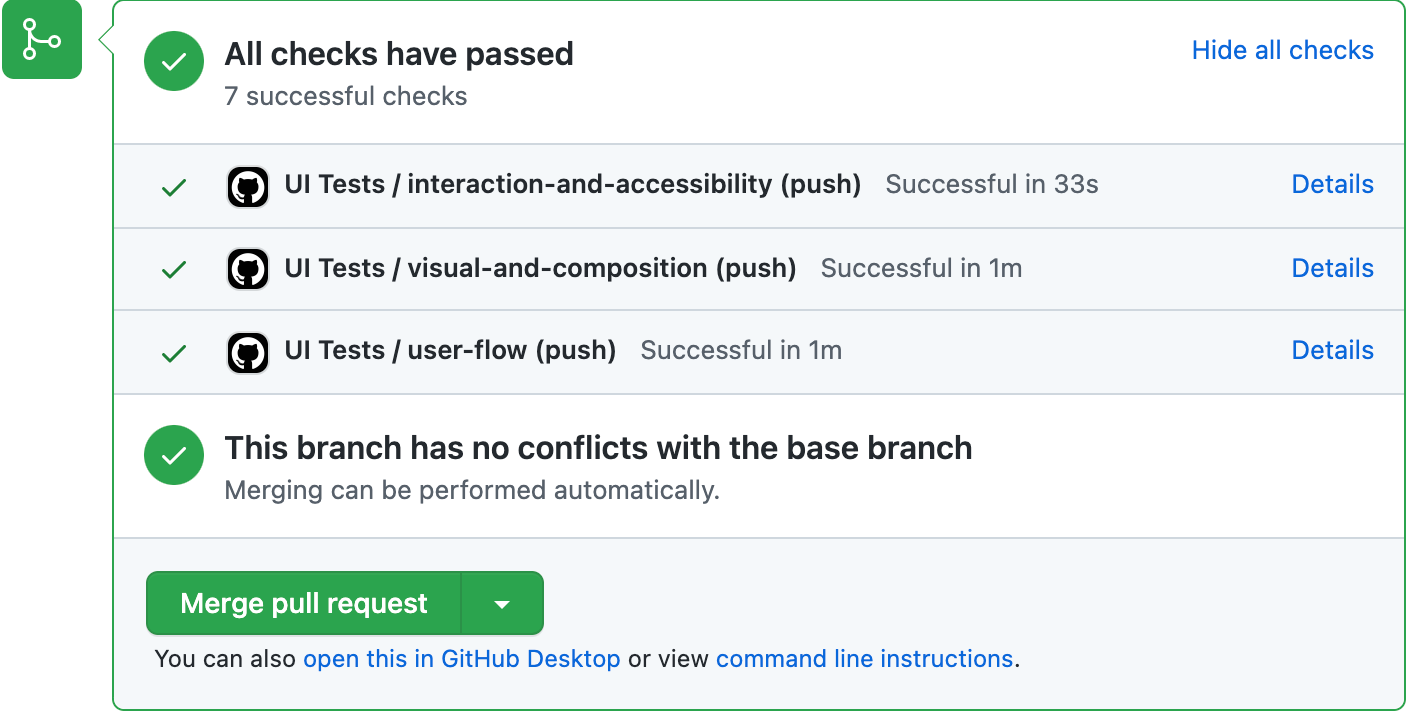
Mastering the UI testing workflow
The testing workflow starts by isolating components using Storybook. Then run checks while you code to get a faster feedback loop. Finally, execute your entire test suite using continuous integration.
Chapter 8 illustrates this complete workflow in action. We'll see how to test a new feature before shipping it to prod.