Test coverage
Test coverage is the practice of measuring whether existing tests fully cover your code. That means surfacing areas which aren't currently being tested, such as: conditions, logic branches, functions and variables.
Coverage tests examine the instrumented code against a set of industry-accepted best practices. They act as the last line of QA to improve the quality of your test suite.
With Storybook Test
When you run component tests with the Test addon, which is powered by Vitest, it can generate a coverage report. The result is summarized in the testing module, showing the percentage of statements covered by your tested stories.
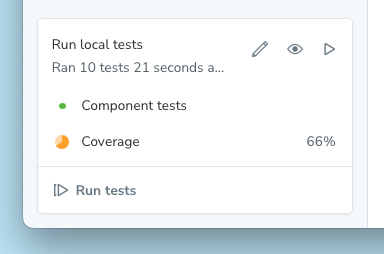
Set up
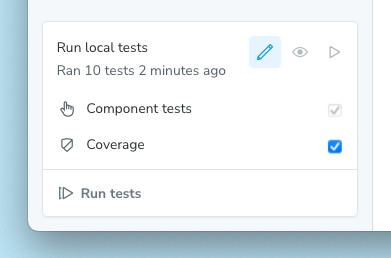
Coverage is included in the Test addon and, when enabled, will be calculated when running component tests for your project. To enable coverage, press the edit button (pencil icon) in the testing module and toggle coverage on:
Before coverage can be calculated, you may need to install a support package corresponding to your coverage provider:
# For v8
npm install --save-dev @vitest/coverage-v8
# For istanbul
npm install --save-dev @vitest/coverage-istanbulAdditionally (until Vitest 3.0.0 is released), the generated coverage report will include the stories files themselves and output from your built Storybook application. This is misleading and they should be excluded. To do this, you can add the following to your Vitest config:
import { coverageConfigDefaults, defineConfig } from 'vitest/config';
export default defineConfig({
// ...
test: {
coverage: {
// 👇 Add this
exclude: [
...coverageConfigDefaults.exclude,
'**/.storybook/**',
// 👇 This pattern must align with the `stories` property of your `.storybook/main.ts` config
'**/*.stories.*',
// 👇 This pattern must align with the output directory of `storybook build`
'**/storybook-static/**',
],
}
}
})Usage
Because coverage is built into the Test addon, you can use it everywhere you run your tests.
Storybook UI
When you enable coverage in the Storybook UI, the coverage report will be generated and summarized in the testing module after you run your tests. You can see the percentage of statements covered by your tested stories, as well as whether the coverage meets the watermarks.
Additionally, the full coverage report will be served at the /coverage/index.html route of your running Storybook.
It's important to understand that the coverage reported in the Storybook UI has three important limitations:
- Coverage is calculated using the stories you've written, not the entire codebase. In other words, it will not include any other Vitest tests.
- Coverage can only be calculated for all stories in your project, not for an individual story or a group of stories.
- Coverage is not calculated while watch mode is activated. When coverage is enabled, enabling watch mode will disable coverage.
CLI
Like the rest of Storybook Test, coverage is built on top of Vitest. Which means you can generate a coverage report using the Vitest CLI.
Assuming you run your tests with a package script like this:
{
"scripts": {
"test-storybook": "vitest --project=storybook"
}
}Then you can generate a coverage report with:
npm run test-storybook -- --coverageThe coverage report will be saved to the configured coverage reports directory (./coverage, by default) in your project.
The above command will only calculate coverage for the stories you've written, not the entire codebase.
Because coverage is most accurate when accounting for all tests in your project, you can also run coverage for all tests in your project with:
npx vitest --coverageEditor extension
Coverage is also available through Vitest's IDE integrations. You can calculate and display coverage results directly in your editor.
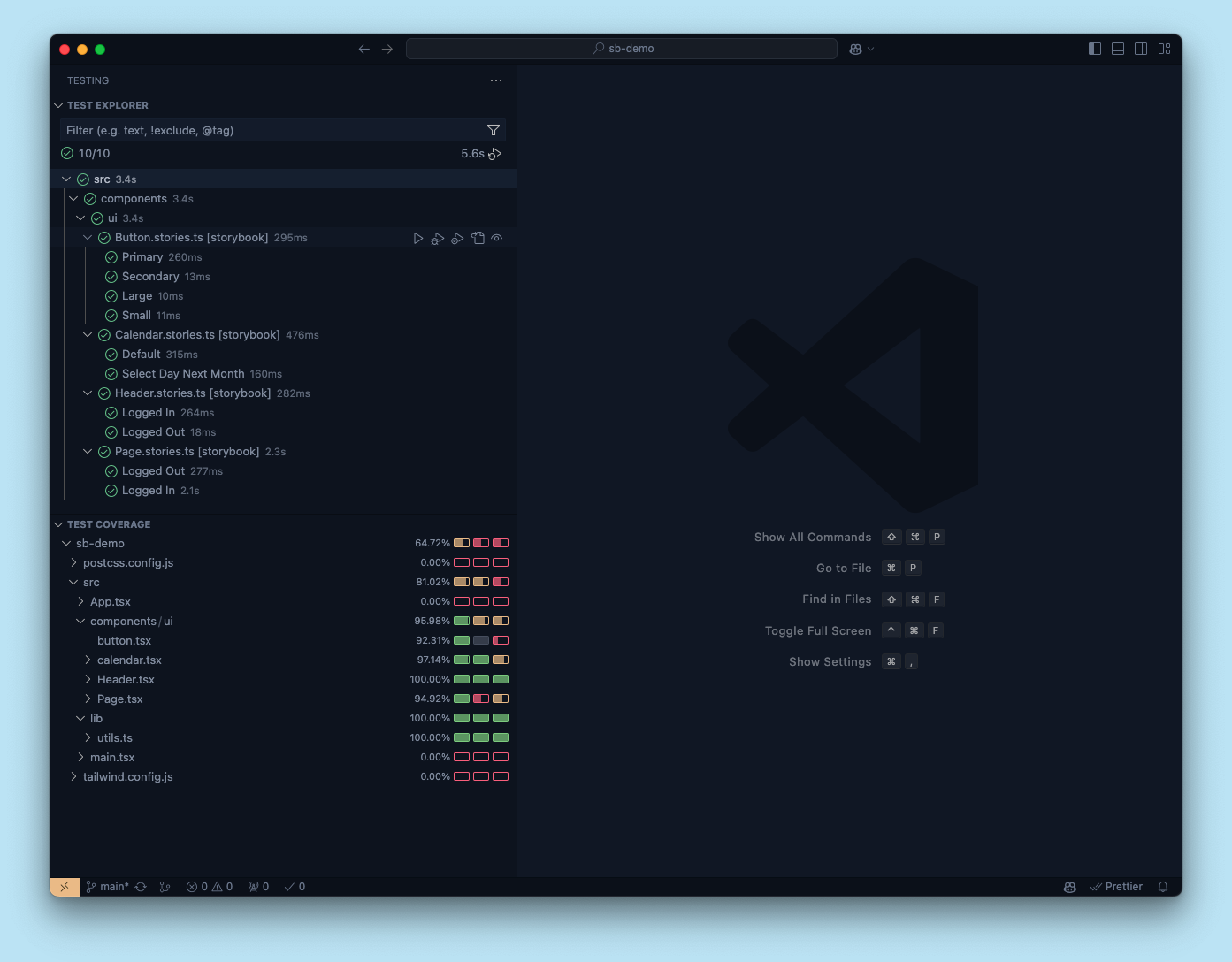
Note that this coverage will include all tests in your project, not just the stories you've written.
CI
To generate coverage reports in your CI pipeline, you can use the CLI.
For example, here's a simplified GitHub Actions workflow that runs your tests and generates a coverage report:
name: Storybook Tests
on: push
jobs:
test:
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: '20.x'
- name: Install dependencies
run: yarn
- name: Run Storybook tests
run: yarn test-storybook --coverageFor more on testing in CI, see the Test addon docs.
Configuration
Coverage provider
You can choose which provider, v8 (default) or Istanbul, to use for coverage calculation by setting the coverage.provider option in your Vitest config:
import { defineConfig } from 'vitest/config';
export default defineConfig({
// ...
test: {
// ...
coverage: {
// ...
provider: 'istanbul', // 'v8' is the default
},
},
});Watermarks
Both coverage providers support watermarks, which are threshold values for coverage. The low watermark is the minimum coverage required to pass the test, and the high watermark is the minimum coverage required to be considered good. A coverage percentage between the low and high watermarks will be considered acceptable but not ideal.
In the testing module, the coverage summary will show the percentage of statements covered by your tested stories, as well as whether the coverage meets the watermarks. Below the low watermark, the icon will be red, between the low and high watermarks, it will be orange, and above the high watermark, it will be green.

To configure the watermarks, you can adjust the Vitest config:
import { defineConfig } from 'vitest/config';
export default defineConfig({
// ...
test: {
// ...
coverage: {
// ...
watermarks: {
// These are the default values
statements: [50, 80],
},
},
},
});Additional configuration
You can find more configuration options for coverage in the Vitest documentation.
When calculating coverage in the Storybook UI, the following options are always ignored:
enabledcleancleanOnRerunreportOnFailurereporterreportsDirectory
With the coverage addon
Watch a video tutorial
Storybook also provides a coverage addon. It is powered by Istanbul, which allows out-of-the-box code instrumentation for the most commonly used frameworks and builders in the JavaScript ecosystem.
Set up
Engineered to work alongside modern testing tools (e.g., Playwright), the coverage addon automatically instruments your code and generates code coverage data. For an optimal experience, we recommend using the test runner alongside the coverage addon to run your tests.
Run the following command to install the addon.
npx storybook@latest add @storybook/addon-coverageThe CLI's add command automates the addon's installation and setup. To install it manually, see our documentation on how to install addons.
Start your Storybook with:
npm run storybookFinally, open a new terminal window and run the test-runner with:
npm run test-storybook -- --coverage
Configure
By default, the @storybook/addon-coverage offers zero-config support for Storybook and instruments your code via istanbul-lib-instrument for Webpack, or vite-plugin-istanbul for Vite. However, you can extend your Storybook configuration file (i.e., .storybook/main.js|ts) and provide additional options to the addon. Listed below are the available options divided by builder and examples of how to use them.
// For Vite support add the following import
// import type { AddonOptionsVite } from '@storybook/addon-coverage';
import type { AddonOptionsWebpack } from '@storybook/addon-coverage';
// Replace your-framework with the framework and builder you are using (e.g., react-webpack5, vue3-webpack5)
import type { StorybookConfig } from '@storybook/your-framework';
const coverageConfig: AddonOptionsWebpack = {
istanbul: {
include: ['**/stories/**'],
exclude: ['**/exampleDirectory/**'],
},
};
const config: StorybookConfig = {
stories: [],
addons: [
// Other Storybook addons
{
name: '@storybook/addon-coverage',
options: coverageConfig,
},
],
};
export default config;Vite options
| Options | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
checkProd | Configures the plugin to skip instrumentation in production environmentsoptions: { istanbul: { checkProd: true,}} | boolean |
cwd | Configures the working directory for the coverage tests. Defaults to process.cwd()options: { istanbul: { cwd: process.cwd(),}} | string |
cypress | Replaces the VITE_COVERAGE environment variable with CYPRESS_COVERAGE.Requires Cypress's code coverage options: { istanbul: { cypress: true,}} | boolean |
exclude | Overrides the default exclude list with the provided list of files or directories to exclude from coverageoptions: { istanbul: { exclude: ['**/stories/**'],}} | Array<String> or string |
extension | Extends the default extension list with the provided list of file extensions to include in coverageoptions: { istanbul: { extension: ['.js', '.cjs', '.mjs'],}} | Array<String> or string |
forceBuildInstrument | Configures the plugin to add instrumentation in build mode options: { istanbul: { forceBuildInstrument: true,}} | boolean |
include | Select the files to collect coverageoptions: { istanbul: { include: ['**/stories/**'],}} | Array<String> or string |
nycrcPath | Defines the relative path for the existing nyc configuration fileoptions: { istanbul: { nycrcPath: '../nyc.config.js',}} | string |
requireEnv | Overrides the VITE_COVERAGE environment variable's value by granting access to the env variablesoptions: { istanbul: { requireEnv: true,}} | boolean |
Webpack 5 options
| Options | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
autoWrap | Provides support for top-level return statements by wrapping the program code in a functionoptions: { istanbul: { autoWrap: true,}} | boolean |
compact | Condenses the output of the instrumented code. Useful for debuggingoptions: { istanbul: { compact: false,}} | boolean |
coverageVariable | Defines the global variable name that Istanbul will use to store coverage resultsoptions: { istanbul: { coverageVariable: '__coverage__',}} | string |
cwd | Configures the working directory for the coverage tests. Defaults to process.cwd()options: { istanbul: { cwd: process.cwd(),}} | string |
debug | Enables the debug mode for additional logging information during the instrumentation processoptions: { istanbul: { debug: true,}} | boolean |
esModules | Enables support for ES Module syntaxoptions: { istanbul: { esModules: true,}} | boolean |
exclude | Overrides the default exclude list with the provided list of files or directories to exclude from coverageoptions: { istanbul: { exclude: ['**/stories/**'],}} | Array<String> or string |
extension | Extends the default extension list with the provided list of file extensions to include in coverageoptions: { istanbul: { extension: ['.js', '.cjs', '.mjs'],}} | Array<String> or string |
include | Select the files to collect coverageoptions: { istanbul: { include: ['**/stories/**'],}} | Array<String> or string |
nycrcPath | Defines the relative path for the existing nyc configuration fileoptions: { istanbul: { nycrcPath: '../nyc.config.js',}} | string |
preserveComments | Includes comments in the instrumented codeoptions: { istanbul: { preserveComments: true,}} | boolean |
produceSourceMap | Configures Instanbul to generate a source map for the instrumented codeoptions: { istanbul: { produceSourceMap: true,}} | boolean |
sourceMapUrlCallback | Defines a callback function invoked with the filename and the source map URL when a source map is generatedoptions: { istanbul: { sourceMapUrlCallback: (filename, url) => {},}} | function |
What about other coverage reporting tools?
Out of the box, code coverage tests work seamlessly with Storybook's test-runner and the @storybook/addon-coverage. However, that doesn't mean you can't use additional reporting tools (e.g., Codecov). For instance, if you're working with LCOV, you can use the generated output (in coverage/storybook/coverage-storybook.json) and create your own report with:
npx nyc report --reporter=lcov -t coverage/storybook --report-dir coverage/storybookTroubleshooting
Run test coverage in other frameworks
If you intend on running coverage tests in frameworks with special files like Vue 3 or Svelte, you'll need to adjust your configuration and enable the required file extensions. For example, if you're using Vue, you'll need to add the following to your nyc configuration file (i.e., .nycrc.json or nyc.config.js):
export default {
// Other configuration options
extension: ['.js', '.cjs', '.mjs', '.ts', '.tsx', '.jsx', '.vue'],
};The coverage addon doesn't support optimized builds
If you generated a production build optimized for performance with the --test flag, and you're using the coverage addon to run tests against your Storybook, you may run into a situation where the coverage addon doesn't instrument your code. This is due to how the flag works, as it removes addons that have an impact on performance (e.g., Docs, coverage addon). To resolve this issue, you'll need to adjust your Storybook configuration file (i.e., .storybook/main.js|ts) and include the disabledAddons option to allow the addon to run tests at the expense of a slower build.
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using (e.g., react-webpack5, vue3-vite)
import type { StorybookConfig } from '@storybook/your-framework';
const config: StorybookConfig = {
framework: '@storybook/your-framework',
stories: ['../src/**/*.mdx', '../src/**/*.stories.@(js|jsx|mjs|ts|tsx)'],
addons: [
'@storybook/addon-essentials',
'@storybook/addon-interactions',
'@storybook/addon-coverage',
],
build: {
test: {
disabledAddons: ['@storybook/addon-docs', '@storybook/addon-essentials/docs'],
},
},
};
export default config;The coverage addon doesn't support instrumented code
As the coverage addon is based on Webpack5 loaders and Vite plugins for code instrumentation, frameworks that don't rely upon these libraries (e.g., Angular configured with Webpack), will require additional configuration to enable code instrumentation. In that case, you can refer to the following repository for more information.
Learn about other UI tests
- Component tests for user behavior simulation
- Visual tests for appearance
- Accessibility tests for accessibility
- Snapshot tests for rendering errors and warnings
- Test runner to automate test execution
- Test coverage for measuring code coverage
- End-to-end tests for simulating real user scenarios
- Unit tests for functionality
