Testing in CI
The Vitest addon is great for automating your UI tests within Storybook. To have full confidence in your work, backed by tests, you need to run those automated tests in your continuous integration (CI) environment.
Thankfully, that’s quite easy!
If you cannot use the Vitest addon in your project, you can still run your stories as tests in CI using the test-runner. Follow the instructions in the test-runner documentation to set up the test-runner to run in CI in your project.
Set up Storybook tests in CI
Running Storybook tests in CI is very similar to running them via CLI on your local machine: you run the same command, just in a different place.
Let’s go step-by-step to set things up.
1. Define package.json script
For convenience, define a script in your package.json to run the Storybook tests. This is the same command you would run locally, but it’s useful to have it in your CI workflow.
{
"scripts": {
"test-storybook": "vitest --project=storybook"
}
}This script calls the vitest CLI command and restricts it to the “storybook” project defined in your Vitest config, which was created when you installed the Vitest addon. (If you’ve renamed the project, adjust the script above accordingly.) You can also pass any additional vitest CLI options you may require.
2. Add a new CI workflow
Next, we’ll create a new “UI Tests” workflow to run in our CI environment. You may also adjust an existing workflow, if you prefer.
Here are some example configurations for popular CI providers:
GitHub Actions
Create a file in the root of your repo, .github/workflow/test-ui.yml:
name: UI Tests
on: [push]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
# Make sure to grab the latest version of the Playwright image
# https://playwright.dev/docs/docker#pull-the-image
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.52.0-noble
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 22.12.0
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Run tests
run: npm run test-storybookGitLab Pipelines
Create a file in the root of your repo, .gitlab-ci.yml:
image: node:jod
stages:
- UI_Tests
cache:
key: $CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG-$CI_PROJECT_DIR
paths:
- .npm/
before_script:
# Install dependencies
- npm ci
Test:
stage: UI_Tests
# Make sure to grab the latest version of the Playwright image
# https://playwright.dev/docs/docker#pull-the-image
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.52.0-noble
script:
- npm run test-storybookBitbucket Pipelines
Create a file in the root of your repo, bitbucket-pipelines.yml:
image: node:jod
definitions:
caches:
npm: $HOME/.npm
pipelines:
default:
- stage:
name: "UI Tests"
steps:
- step:
name: "Run Tests"
# Make sure to grab the latest version of the Playwright image
# https://playwright.dev/docs/docker#pull-the-image
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.52.0-noble
caches:
- npm
- node
script:
# Install dependencies
- npm ci
- npm run test-storybookCircle CI
Create a file in the root of your repo, .circleci/config.yml:
version: 2.1
executors:
ui-testing:
docker:
# Make sure to grab the latest version of the Playwright image
# https://playwright.dev/docs/docker#pull-the-image
- image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.52.0-noble
working_directory: ~/repo
jobs:
Test:
executor: ui-testing
steps:
- checkout
- restore_cache:
keys:
- v1-dependencies-{{ checksum "package-lock.json" }}
- v1-dependencies-
# Install dependencies
- run: npm ci
- run: npm run test-storybook
- save_cache:
name: Save NPM cache
paths:
- ~/.npm
key: v1-dependencies-{{ checksum "package-lock.json" }}
workflows:
UI_Tests:
jobs:
- TestTravis CI
Create a file in the root of your repo, .travis.yml:
language: node_js
os: linux
dist: jammy
node_js:
- 20
before_script:
# Install dependencies and Playwright browsers so Vitest browser mode can run story tests
- npm ci && npm run playwright install chromium --with-deps
cache: npm
jobs:
include:
- stage: "UI Tests"
name: "Run tests"
script: npm run test-storybookJenkins
Create a file in the root of your repo, JenkinsFile:
pipeline {
agent any
tools {nodejs "node"}
stages {
stage('UI Tests'){
agent {
docker {
/*
* Make sure to grab the latest version of the Playwright image
* https://playwright.dev/docs/docker#pull-the-image
*/
image 'mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.52.0-noble'
reuseNode true
}
}
steps {
/* Install dependencies */
sh 'npm ci'
sh "npm run test-storybook"
}
}
}
}Azure Pipelines
Create a file in the root of your repo, azure-pipelines.yml:
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: "ubuntu-latest"
stages:
- stage: UI_Tests
displayName: "UI Tests"
jobs:
- job: Test
displayName: "Storybook tests"
# Make sure to grab the latest version of the Playwright image
# https://playwright.dev/docs/docker#pull-the-image
container: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.52.0-noble
variables:
npm_config_cache: $(Pipeline.Workspace)/.npm
steps:
- task: UseNode@1
displayName: "Install Node.js"
inputs:
version: "22.12.0"
- task: Cache@2
displayName: "Install and cache dependencies"
inputs:
key: 'npm | "$(Agent.OS)" | package-lock.json'
restoreKeys: |
npm | "$(Agent.OS)"
path: $(npm_config_cache)
- script: npm ci
condition: ne(variables.CACHE_RESTORED, 'true')
- task: CmdLine@2
displayName: "Run tests"
inputs:
script: npm run test-storybookStorybook Test uses Playwright to render your stories by default. For the fastest experience, you should use a machine image that has Playwright already installed (as in most of the snippets above).
2.1 Debug test failures
When a Storybook test fails, the failure output includes a link to the failing story. When running locally, this points to your local Storybook running at localhost:6006. But in CI, there is no active Storybook. Instead, you must first build and publish your Storybook, then inform the Vitest addon where your Storybook is published so that it can print useful story links.
Here's an example using GitHub Actions. The steps are similar for other CI providers, though details in the syntax or configuration may vary.
When deployments for services like Vercel, GitHub Pages, and others are performed, they follow a pattern of emitting a deployment_status event containing the newly generated URL under deployment_status.environment_url. This is the URL to the published Storybook instance.
We can pass that URL to the command using an environment variable, SB_URL.
name: Storybook Tests
+ # 👇 Update this to only run when a deployment status is emitted
+ on: deployment_status
- on: [push]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.52.0-noble
+ # 👇 Only run on successful deployments
+ if: github.event_name == 'deployment_status' && github.event.deployment_status.state == 'success'
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 22.12.0
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Run tests
run: npm run test-storybook
+ # 👇 Pass the Storybook URL as an environment variable
+ env:
+ SB_URL: '${{ github.event.deployment_status.environment_url }}'Finally, we update the plugin configuration to use that environment variable in the storybookUrl plugin option.
export default defineConfig({
// ...
test: {
// ...
projects: [
{
plugins: [
storybookTest({
// ...
// 👇 Use the environment variable you passed
storybookUrl: process.env.SB_URL,
}),
],
},
],
},
});Now, when a test fails in CI, the printed story URL will point to the published Storybook, making debugging that failure a breeze!
2.2 Calculate code coverage
For more details on code coverage, check the full guide.
You can calculate code coverage of your Storybook tests by passing the --coverage flag to the vitest command. Coverage is most useful when calculated comprehensively across all tests in your project, but you can also calculate it for just the Storybook tests.
You can either adjust the command in your package.json scripts:
For all tests:
{
"scripts": {
+ "test": "vitest --coverage"
- "test": "vitest"
}
}For only Storybook tests:
{
"scripts": {
+ "test-storybook": "vitest --project=storybook --coverage"
- "test-storybook": "vitest --project=storybook"
}
}Or, if you only want to calculate coverage when running tests in CI, adjust your CI configuration like so:
For all tests:
+ npm run test -- --coverage
- npm run testFor only Storybook tests:
+ npm run test-storybook -- --coverage
- npm run test-storybook3. Run your workflow
Assuming your CI is configured to run when you push your work to a pull request, you can test your new workflow by creating a new pull request (perhaps to fix an accessibility issue found by Storybook Test).
When you do so, you should see the test result as a status check on the pull request screen. For example, in GitHub, a failing test run would look something like this:
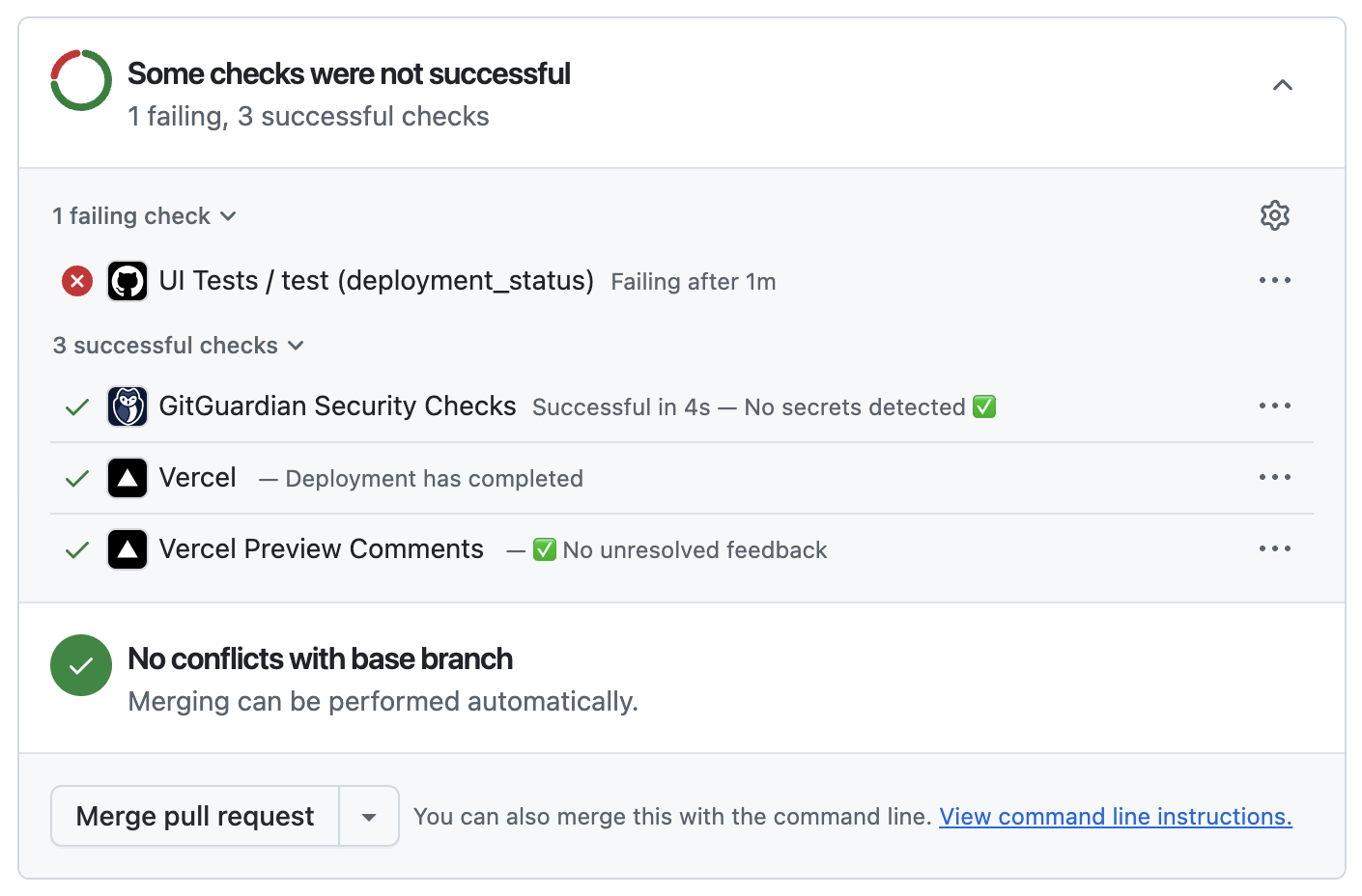
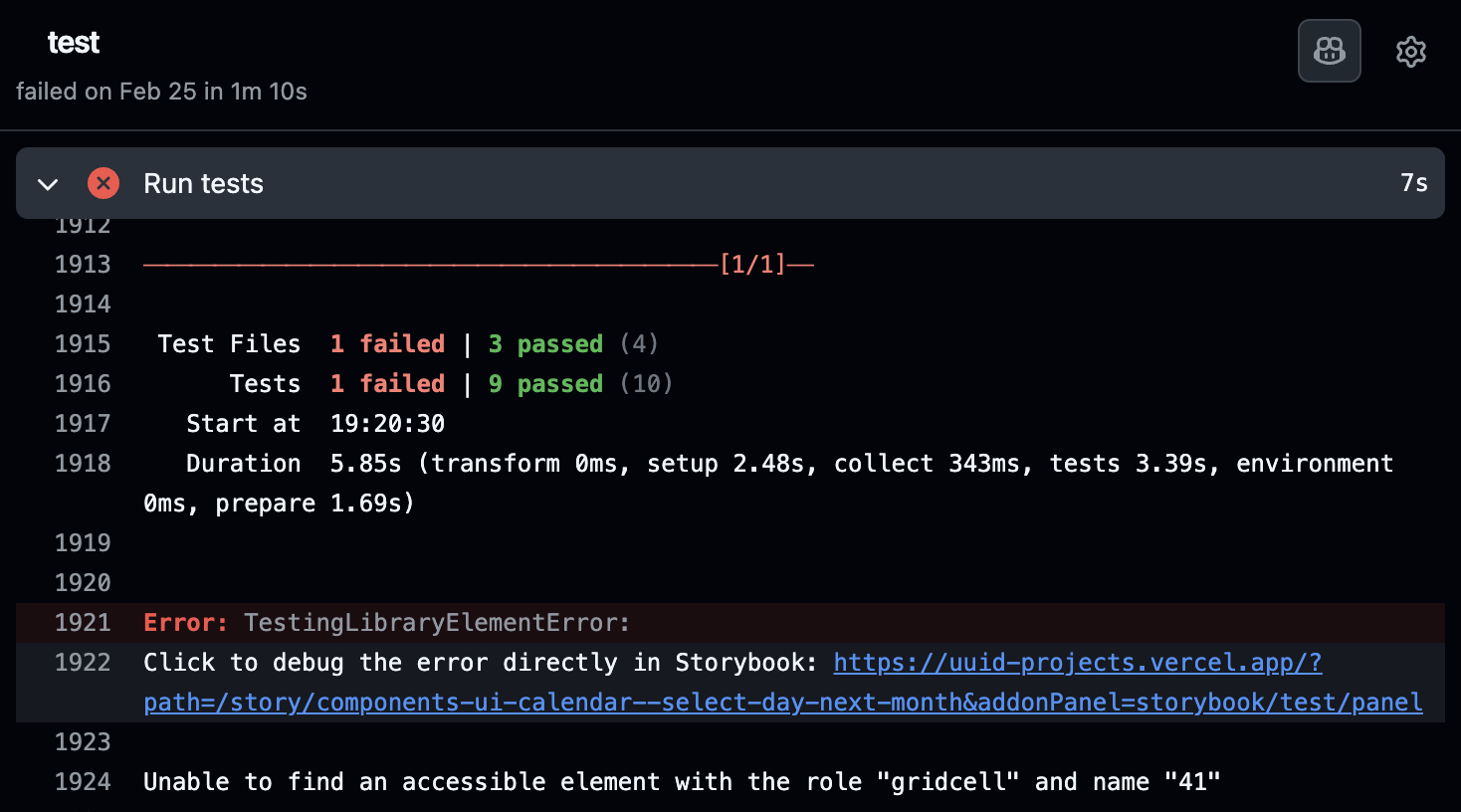
Clicking on the failure will take you to the full test output, including the link to the failing story (if you've set up the SB_URL environment variable).
FAQs
How do I run other Vitest tests alongside my Storybook tests?
Some projects have other tests run via Vitest, e.g. unit tests, in addition to those defined in Storybook.
You can run these tests independently by specifying the project filter in a separate script. For example, for a Vitest project called “unit”:
{
"scripts": {
"test-storybook": "vitest --project=storybook",
"test-unit": "vitest --project=unit"
}
}Then, in your workflow, call this script alongside the Storybook one:
- name: Run tests
run: |
npm run test-unit
npm run test-storybookYou may also choose to run all tests together by simply omitting the --project=storybook filter from the package.json script:
{
"scripts": {
"test": "vitest"
}
}The workflow would then look like:
- name: Run tests
run: |
npm run testMore testing resources
- Vitest addon for running tests in Storybook
- Interaction testing for user behavior simulation
- Accessibility testing for accessibility
- Visual testing for appearance
- Snapshot testing for rendering errors and warnings
- Test coverage for measuring code coverage
- End-to-end testing for simulating real user scenarios
- Unit testing for functionality
- Test runner to automate test execution
